早安英文安卓版

- 文件大小:62.08MB
- 界面语言:简体中文
- 文件类型:Android
- 授权方式:5G系统之家
- 软件类型:装机软件
- 发布时间:2024-11-05
- 运行环境:5G系统之家
- 下载次数:484
- 软件等级:
- 安全检测: 360安全卫士 360杀毒 电脑管家
系统简介
Introduction to the Versatile Vine: A Botanical Marvel

Vines are a fascinating group of plants that have captured the imagination of humans for centuries. Known for their ability to climb and sprawl, vines are found in a variety of environments across the globe. This article delves into the characteristics, uses, and significance of vines in both natural and human-made settings.
Botanical Characteristics of Vines

Vines are a diverse group of plants that belong to the botanical family Vitaceae. They are characterized by their long, slender stems that can grow either as lianas (which climb by wrapping around supports) or as trailing plants (which spread along the ground). Vines have a unique growth habit, often producing tendrils or aerial roots that help them attach to and climb their supports.
Types of Vines

There are numerous types of vines, each with its own distinct features. Some of the most common types include:
- Grapes: Known for their edible fruits, grapes are a popular type of vine.
- Wisteria: Known for its fragrant flowers, Wisteria vines are often used in gardens for their beauty.
- Ipomoea (Morning Glory): These vines produce vibrant flowers that bloom in the morning and fade by evening.
- Hedera helix (English Ivy): A popular choice for ground cover and climbing walls, English ivy is also known for its ability to clean indoor air.
Environmental Adaptations
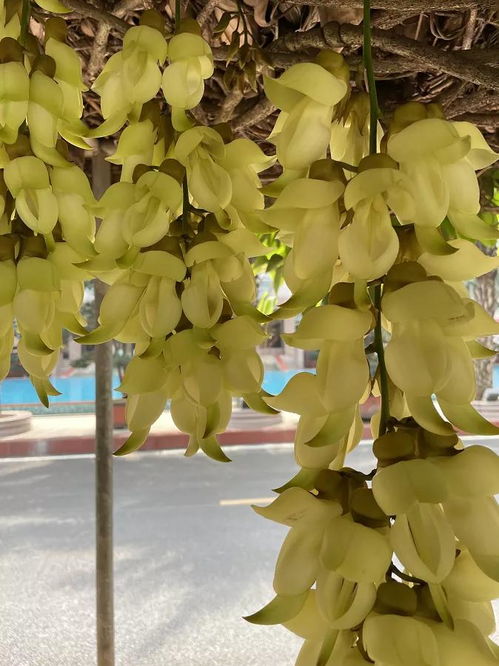

Vines have evolved a variety of adaptations to thrive in different environments. Their ability to climb allows them to reach sunlight, which is crucial for photosynthesis. Additionally, vines often have tendrils or aerial roots that help them attach to and climb their supports, such as trees, buildings, or other plants.
Ecological Roles

Vines play a significant role in ecosystems. They provide habitat and food for a variety of animals, including birds, insects, and mammals. Vines also contribute to soil stability by holding the ground together with their roots. In some cases, vines can even help to restore degraded ecosystems by preventing soil erosion and promoting the growth of other plants.
Cultural Significance

Vines have held cultural significance in various societies throughout history. In many cultures, vines are associated with fertility, abundance, and life. For example, in Greek mythology, the vine is a symbol of Dionysus, the god of wine and festivity. In other cultures, vines are used in religious ceremonies and rituals.
Practical Uses of Vines

Apart from their aesthetic appeal, vines have practical uses. They are commonly used in landscaping to create natural screens, provide shade, and add visual interest to gardens. Vines can also be used to create living walls and green roofs, which help to improve air quality and reduce energy consumption.
Challenges and Concerns

While vines have many benefits, they can also pose challenges. Some vines can become invasive, outcompeting native plants and disrupting local ecosystems. Additionally, certain vines can cause damage to structures, such as buildings and bridges, as they grow and climb.
Conclusion

Vines are a remarkable group of plants that have adapted to a wide range of environments and have played a significant role in both natural and human-made settings. Their ability to climb, adapt, and provide numerous benefits makes vines a fascinating subject of study and appreciation. Whether in the wild or in our gardens, vines continue to captivate us with their beauty and utility.
常见问题
- 2025-12-19 同仁追剧免费播放完整版
- 2025-12-18 真实枪械模拟器
- 2025-12-18 怎么样才能不当社畜:妻子的故事
- 2025-12-18 皮卡漫画最新版下载
装机软件下载排行

其他人正在下载
- 天体数藏app
- 液多多商户版
- 旺店通旗舰版手机版
- 小滴云手机官网版
- 小狐狸官方手机钱包
- tokenpocket官网下载
- Cobo钱包官网版
- tokenim官网下载
- TronLink正版钱包
- Math Wallet钱包官网版