python获取当前系统时间, 使用`datetime`模块获取当前时间
时间:2024-11-28 来源:网络 人气:
Python获取当前系统时间详解
在编程过程中,获取当前系统时间是一个基本且常用的操作。Python提供了多种方式来获取当前时间,包括使用标准库中的`datetime`模块和`time`模块。本文将详细介绍如何在Python中获取当前系统时间,并探讨不同方法的特点和适用场景。
使用`datetime`模块获取当前时间

导入`datetime`模块
首先,我们需要导入Python的`datetime`模块,这是Python标准库的一部分,无需额外安装。
```python
import datetime
获取当前时间
使用`datetime`模块的`datetime.now()`函数可以获取当前的日期和时间。
```python
current_time = datetime.datetime.now()
print(current_time)
格式化时间
`datetime`对象可以很容易地转换为字符串,并且可以指定格式。
```python
formatted_time = current_time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
print(formatted_time)
使用`time`模块获取当前时间
导入`time`模块
`time`模块同样不需要安装,可以直接使用。
```python
import time
获取当前时间戳
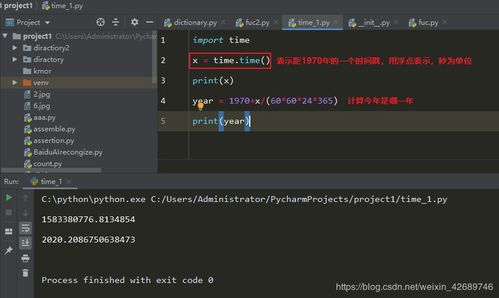
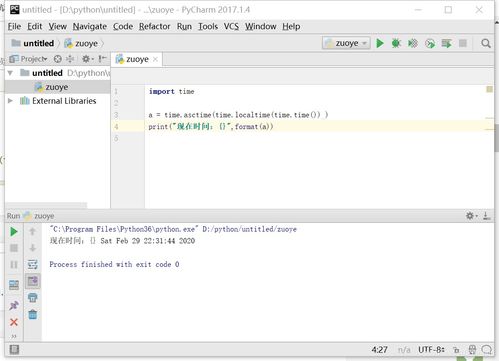
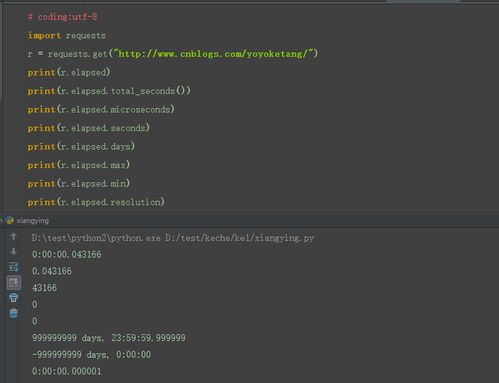
`time`模块的`time.time()`函数返回当前时间的时间戳,即从1970年1月1日00:00:00 UTC到当前时间的秒数。
```python
timestamp = time.time()
print(timestamp)
将时间戳转换为本地时间
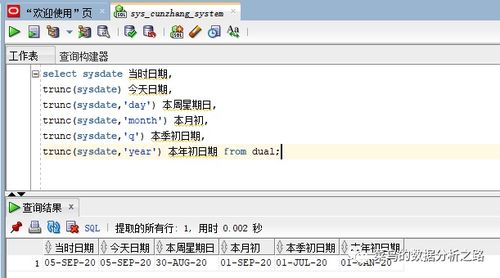
`time`模块的`time.localtime()`函数可以将时间戳转换为本地时间。
```python
local_time = time.localtime(timestamp)
print(local_time)
格式化时间

与`datetime`模块类似,`time`模块也可以格式化时间。
```python
formatted_time = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', local_time)
print(formatted_time)
使用`datetime`模块获取特定格式的时间
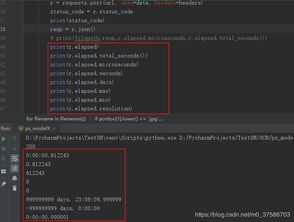
获取当前日期

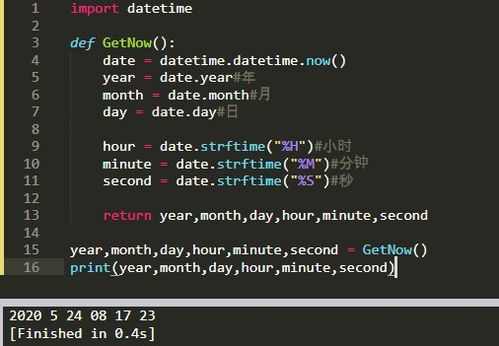
使用`datetime`模块的`datetime.date.today()`函数可以获取当前的日期。
```python
current_date = datetime.date.today()
print(current_date)
获取当前时间
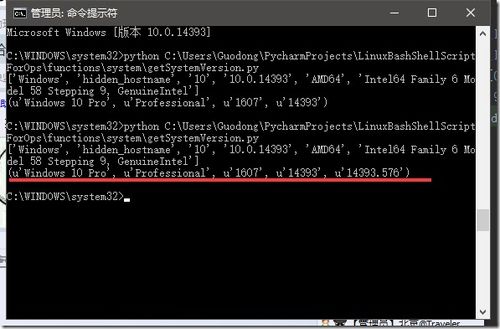
使用`datetime.datetime.now().time()`可以获取当前的时间。
```python
current_time = datetime.datetime.now().time()
print(current_time)
使用`time`模块获取特定格式的时间
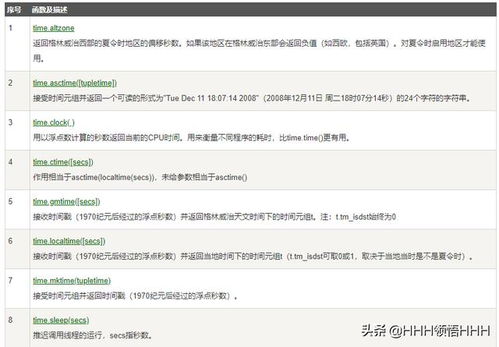
获取当前日期
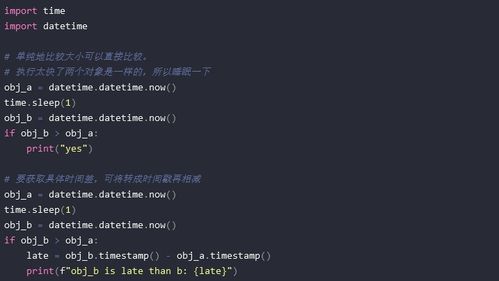
`time`模块的`time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d', time.localtime())`可以获取当前的日期。
```python
current_date = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d', time.localtime())
print(current_date)
获取当前时间
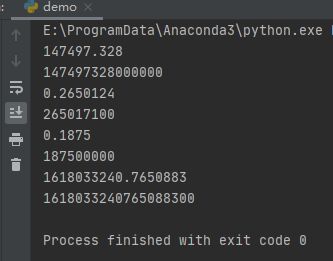
`time`模块的`time.strftime('%H:%M:%S', time.localtime())`可以获取当前的时间。
```python
current_time = time.strftime('%H:%M:%S', time.localtime())
print(current_time)
教程资讯
教程资讯排行